Basic Electrical Theory
Basic Electrical Theory
Electrical charges:-
Charge is an electrical property of the atomic particles of which matter consists, measured in coulombs (C).
• The charge e on one electron is negative and equal in magnitude to 1.602 × 10-19 C which is called as electronic charge. The charges that occur in nature are integral multiples of the electronic charge.
Electrical Current:-
Electric current i = dq/dt. The unit of ampere can be derived as 1 A = 1C/s.
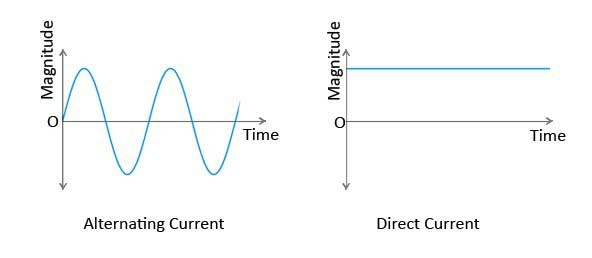
• A direct current (dc) is a current that remains constant with time.
• An alternating current (ac) is a current that varies sinusoidally with time.
Example 1
A conductor has a constant current of 5 A. How many electrons pass a fixed point on the conductor in one minute?
Solution
Total no. of charges pass in 1 min is given by 5 A = (5 C/s)(60 s/min) = 300 C/min
Electric Voltage:-
• Voltage (or potential difference) is the energy required to move
a unit charge through an element, measured in volts (V).
• Mathematically, (volt)
– w is energy in joules (J) and q is charge in coulomb (C).
• Electric voltage, vab, is always across the circuit element or
between two points in a circuit.
vab > 0 means the potential of a is higher than potential of b.
vab < 0 means the potential of a is lower than potential of b.
Power and Energy
Power
Power is the time rate of expending or absorbing energy,
measured in watts (W).
• Mathematical expression:
P=V ×I (P=Power,V=Voltage,I=Current)
Passive sign convention
P = +vi p = –vi
absorbing power supplying power
Energy
The law of conservation of energy
∑ p = 0
• Energy is the capacity to do work, measured in joules (J).
Electrical charges:-
Charge is an electrical property of the atomic particles of which matter consists, measured in coulombs (C).
• The charge e on one electron is negative and equal in magnitude to 1.602 × 10-19 C which is called as electronic charge. The charges that occur in nature are integral multiples of the electronic charge.
Electrical Current:-
Electric current i = dq/dt. The unit of ampere can be derived as 1 A = 1C/s.
• A direct current (dc) is a current that remains constant with time.
• An alternating current (ac) is a current that varies sinusoidally with time.
Example 1
A conductor has a constant current of 5 A. How many electrons pass a fixed point on the conductor in one minute?
Solution
Total no. of charges pass in 1 min is given by 5 A = (5 C/s)(60 s/min) = 300 C/min
Electric Voltage:-
• Voltage (or potential difference) is the energy required to move
a unit charge through an element, measured in volts (V).
• Mathematically, (volt)
– w is energy in joules (J) and q is charge in coulomb (C).
• Electric voltage, vab, is always across the circuit element or
between two points in a circuit.
vab > 0 means the potential of a is higher than potential of b.
vab < 0 means the potential of a is lower than potential of b.
Power and Energy
Power
Power is the time rate of expending or absorbing energy,
measured in watts (W).
• Mathematical expression:
P=V ×I (P=Power,V=Voltage,I=Current)
Passive sign convention
P = +vi p = –vi
absorbing power supplying power
Energy
The law of conservation of energy
∑ p = 0
• Energy is the capacity to do work, measured in joules (J).


Comments
Post a Comment